Last Updated on 2025-10-16 by BallPen
삼각함수의 여각공식에 대해 알아 봐요.
1. 여각 공식
어느 각도를 \theta라할 때 이 각도의 여각(complementary angle)은 ( \pi / 2 - \theta)입니다. 그래서 어느 각과 그 여각을 합하면 아래 (1)식처럼 \pi \over 2 rad이 되는 거에요.
\tag{1}
\theta + ({\pi \over 2} - \theta) = {\pi \over 2}그런데 이러한 여각끼리의 관계가 삼각함수에서 항등식으로 나타나는 경우가 있습니다.
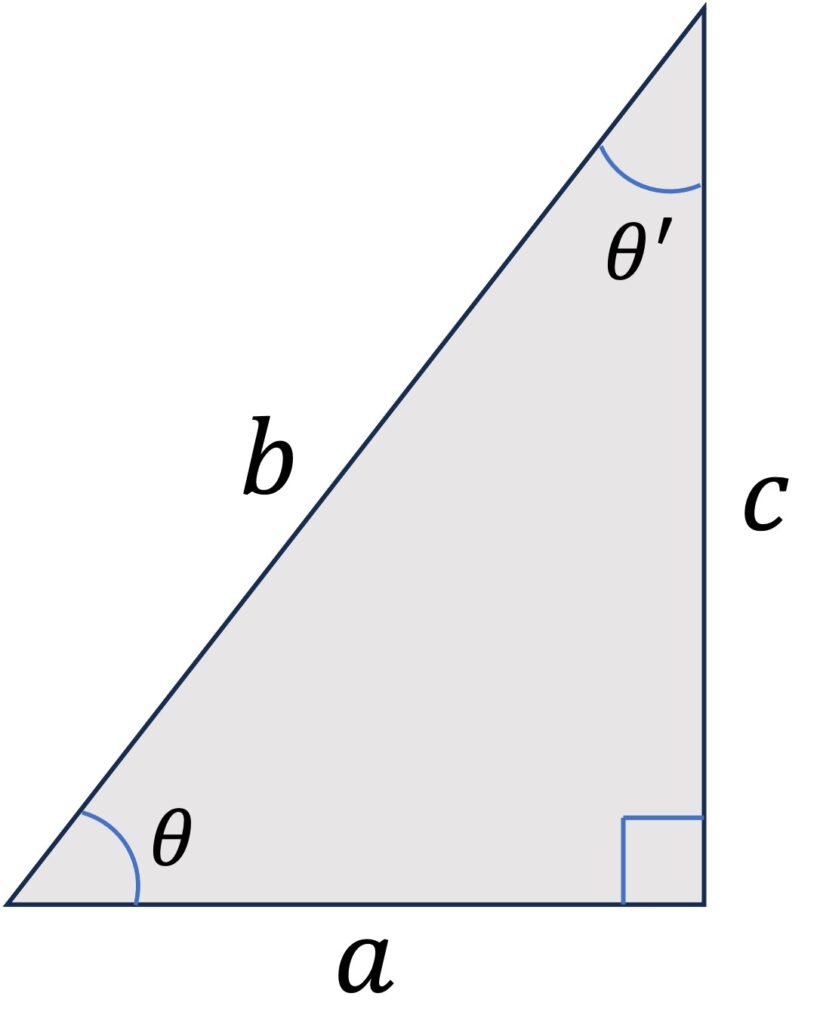
[그림 1]의 직각삼각형이 있을 때 직각을 제외한 한 각도를 \theta라 하면 나머지 한 각도 \theta^{\prime}은 ( \pi/2 - \theta)가 되어 여각이 된다는 것을 알 수 있어요.
\tag{2}
\begin{align}
\pi = \theta+\theta^{\prime} +{\pi \over 2}
\end{align}\tag{3}
\begin{align}
\theta^{\prime} = {\pi \over 2} - \theta
\end{align}그런데 한 삼각함수에 \theta를 취했을 때와 다른 삼각함수에 그 여각인 {\pi \over 2} - \theta를 취했을 때 그 값들이 서로 같아지는 경우가 있어요.
예를 들어, [그림 1]의 직각삼각형을 참고하면 다음 관계가 성립함을 알 수 있어요.
\tag{4}
\begin{aligned}
&\sin (\theta)= \cos(\theta^{\prime}) = \cos({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta)\\[10pt]
&\cos(\theta) = \sin(\theta^{\prime}) = \sin({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta)\\[10pt]
&\tan (\theta) = \cot(\theta^{\prime})=\cot({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta) \\[10pt]
&\cot (\theta) = \tan(\theta^{\prime})=\tan({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta) \\[10pt]
&\sec (\theta) = \csc(\theta^{\prime})=\csc({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta) \\[10pt]
&\csc (\theta) = \sec(\theta^{\prime})=\sec({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta) \\
\end{aligned}이와 같이 sin\leftrightarrowcos, tan\leftrightarrowcot, sec\leftrightarrowcsc가 서로 대응하여 서로 여각이 취해질 때 같은 함수 값을 갖게 됩니다.
이 공식을 삼각함수의 여각공식이라고 해요. 참고로 코사인, 코탄젠트, 코시컨트의 ‘코’는 complementary의 co를 뜻해요.
2. 증명
tan 에 대한 여각 공식을 증명해 봐요.
\tag{5}
\begin{aligned}
\tan({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta) &= {{\sin({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta)}\over{\cos({{\pi}\over{2}}-\theta)}}\\[10pt]
&={{\sin{\pi \over 2} \cos \theta - \cos{{\pi}\over{2}}\sin\theta}\over{\cos{\pi \over 2}} \cos \theta + \sin{{\pi}\over{2}}\sin \theta}\\[10pt]
&={{\cos \theta}\over{\sin \theta}}\\[10pt]
&=\cot \theta
\end{aligned}흥미롭고 도움이 되는 글이었나요? 리뷰를 부탁드립니다.
[Total: 1 Average: 5]

오늘도 좋은 글 감사합니다 !
방문해 주셔서 감사합니다.